ArcGIS
ArcGIS
ArcGIS is a geographic information system (GIS) for working with maps and geographic information. It is used for: creating and using maps; compiling geographic data; analyzing mapped information; sharing and discovering geographic information; using maps and geographic information in a range of applications; and managing geographic information in a database.
The first thing that we did was import all of the data that we needed from the digimaps platform. This includeded building heights, topography and other geographic data which we would later composite.
We then began the process of importing this data into the ArcGIS program and compositing it into a single data set an ArcCatalog.
We then used the Data Frame Properties tool to overlay historic site data. All ArcGIS data contains location metadata within it which means its real world position does not need to be manually imputed, the program already knows where to position the data.
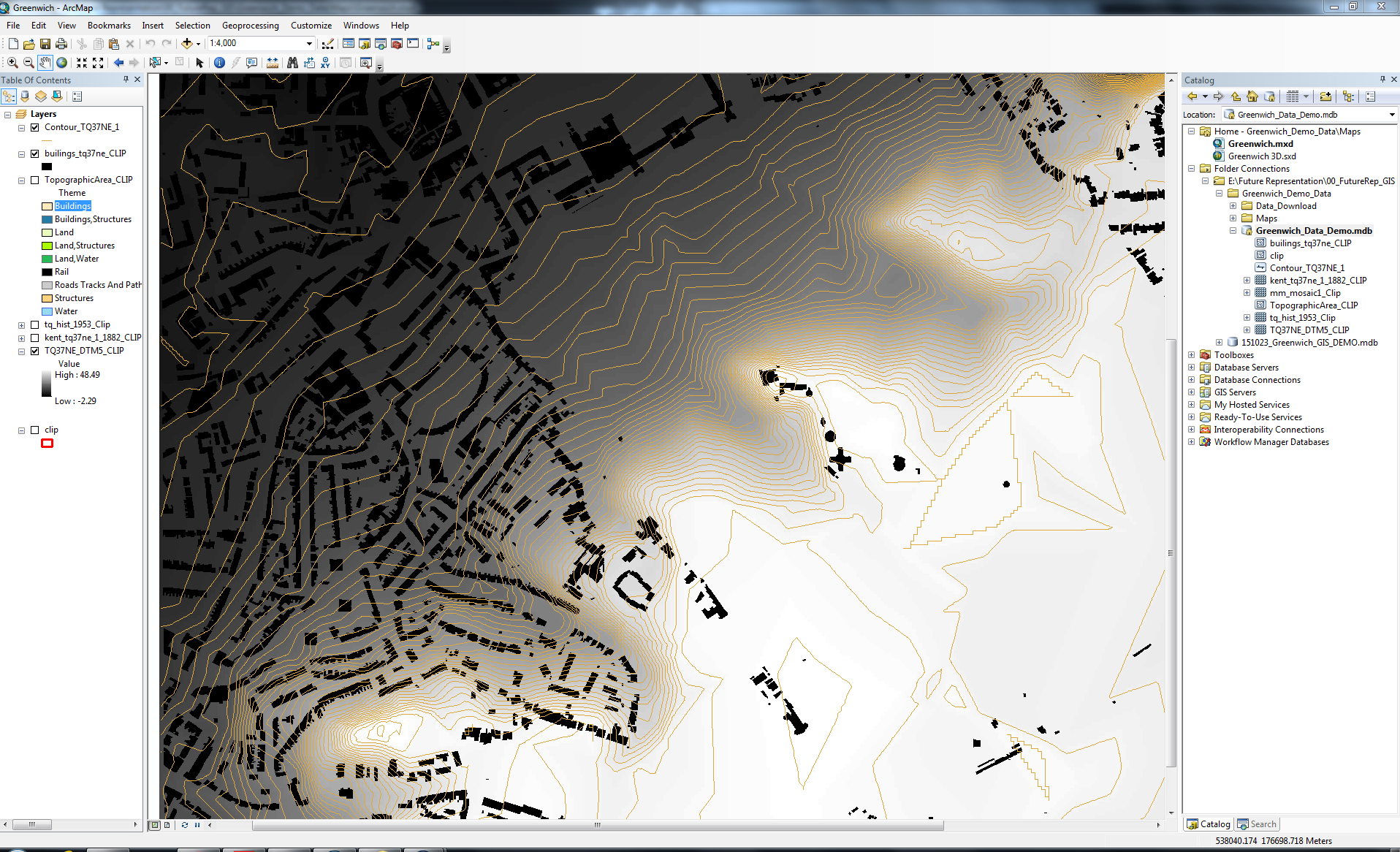
The digimap data, having been packaged together in ArcCatalog, was imported into ArcMap for data analysis and presentation. Shown above is the raw topography and building footprint data.
ArcMap includes tools for the presentation and printing of geographical data. Here we experimented with the poitioning and scale of a rudimentary map on a page.
ArcMap also has several default data presentation templates for quick printing. Shown above is one such template in use on our data showing greenwich.
Using the information from the ArcGIS workshop I was able to create a topography and building height data set showing the larger context of my studio site. This model then formed the basis for several mapping and analysis exercises for my studio project.